The Full Guide to Healthcare Software Development Services



Over recent years, the healthcare industry has undergone a huge digital transformation due to the need to completely update its existing infrastructure. The pandemic and other factors — one of which is an increased desire for patients to take an active role in their own healthcare process — have accelerated the transition of offline medical services to digital, resulting in the need for secure, interoperable, and compliant software solutions. This is the perfect time for the healthcare tech industry, as there has never been such high demand for quality products as there is today.
If you’re a healthcare startup looking to transform patient care digitally and optimize your operations, you’ve come to the right place. In this article, we will discuss the realm of healthcare software development services and delve into everything you need to drive success for your startup.
Content
Medical protocols are being moved to digital and virtual care as well as customized cloud-based services, resulting in a growing amount of healthcare data and a growing need for innovative technology. The healthcare market’s stakeholders and participants must recognize these emerging trends and adapt quickly to this new environment.
Health-related startups should seize this change as a chance to introduce new products and business models. However, investments in the health technology market have continued to grow despite a freeze in patient spending on medical services during this time.
It should be noted that for healthcare software development security standards and certifications serve as crucial pillars. Let’s delve into these important aspects.
By complying with healthcare regulations, healthcare startups can confidently navigate the digital landscape while prioritizing patient confidentiality and data integrity.
HITRUST: It created the Common Security Framework (CSF) to address the complex web of healthcare regulations and standards. HITRUST CSF consolidates various security and privacy frameworks, including HIPAA, ISO 27001, and NIST, into a comprehensive framework tailored to the healthcare industry. It provides a roadmap for implementing controls, conducting risk assessments, and ensuring compliance. Achieving HITRUST CSF certification demonstrates a healthcare startup’s commitment to protecting patient data and aligning with industry best practices. It is often considered a gold standard for healthcare software security, reassuring healthcare providers and patients.
HIPAA: As a landmark regulation in the United States, sets the standard for sensitive patient health information (PHI). HIPAA mandates security and privacy rules that healthcare software must adhere to. The Security Rule outlines administrative, physical, and technical safeguards to protect electronic PHI (ePHI). It covers access controls, encryption, data backups, incident response, and employee training. Compliance with HIPAA ensures data security and helps healthcare startups avoid hefty penalties for non-compliance.
GDPR: Although GDPR is a European Union regulation, its impact is felt worldwide due to its extraterritorial reach. GDPR focuses on protecting EU residents’ privacy and personal data, including healthcare-related information. Healthcare software that deals with EU residents’ data must comply with GDPR requirements, such as obtaining explicit consent, implementing data minimization and pseudonymization techniques, conducting privacy impact assessments, and notifying authorities of data breaches within a specified timeframe. Adhering to GDPR not only protects patient data but also enhances the reputation and trustworthiness of healthcare startups.
ISO 27001: It is an ISMS standard internationally recognized information security management system (ISMS) standard. It systematically manages sensitive information, including implementing security controls, risk assessment, and continuous improvement. Achieving ISO 27001 certification demonstrates a healthcare startup’s commitment to maintaining a robust security framework. It helps identify vulnerabilities, mitigate risks, and ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and availability. ISO 27001 certification enhances healthcare software’s credibility, instills patient confidence, and positions startups as security-conscious organizations.
NIST: Special Publication 800-53 concerns a framework for securing sensitive information systems, including those in the healthcare sector. It covers various security controls and practices, addressing access control, incident response, encryption, and security awareness training. Adhering to NIST standards helps healthcare startups enhance their security posture, protect patient data, and align with industry best practices.
Healthcare industry digitalization is estimated to reach $379 billion by 2024. As technology and innovations evolve, health software development is getting more complex. A lot of features are being added to sustain the individual needs of medical staff and their patients.
AI is expected to have a positive impact on the healthcare industry and help it meet these new sector requirements in the future. When it comes to medical services, artificial intelligence has a wide range of potential applications, and some of its capabilities are already being utilized.
Administrative tasks and paperwork assistance, which can be implemented quickly, have the ability to be scaled up to more complex impact areas that require greater time, research, and trials. All application areas are scalable. AI has tremendous optimization potential for the healthcare industry, despite some challenges.
All of these enhancements ultimately lead to a better quality of medical services for patients, as they receive more accurate diagnostics and faster responses from doctors, and significantly improve working conditions for medical staff. Artificial intelligence solutions can result in many saved lives and a reduction in costs spent on healthcare services for both service providers and receivers.
With many factors driving transformation across the industry, it is anticipated to rapidly evolve and adapt new technologies to sustain changing demands. Here is a case study that shows how Glorium did exactly this.
From teaching medical students to creating treatment simulations, virtual and augmented reality technology is used in the healthcare industry in a variety of ways. VR and AR are often mistaken for the same technology, but they are actually quite different and have a variety of applications in medicine. According to Allied Market Research, the market for virtual and augmented reality products in healthcare is anticipated to reach $2.4 billion by 2026.
Virtual layers and projections can be added to existing physical objects in augmented reality. Because of this, AR-enabled products are ideal for advanced human body studies, visualizing specific body parts and treatment processes for patients, and assisting doctors in making treatment decisions, preparing for surgery, and anticipating the body’s response.
Check how Glorium Technologies builds healthcare apps with AR mode.
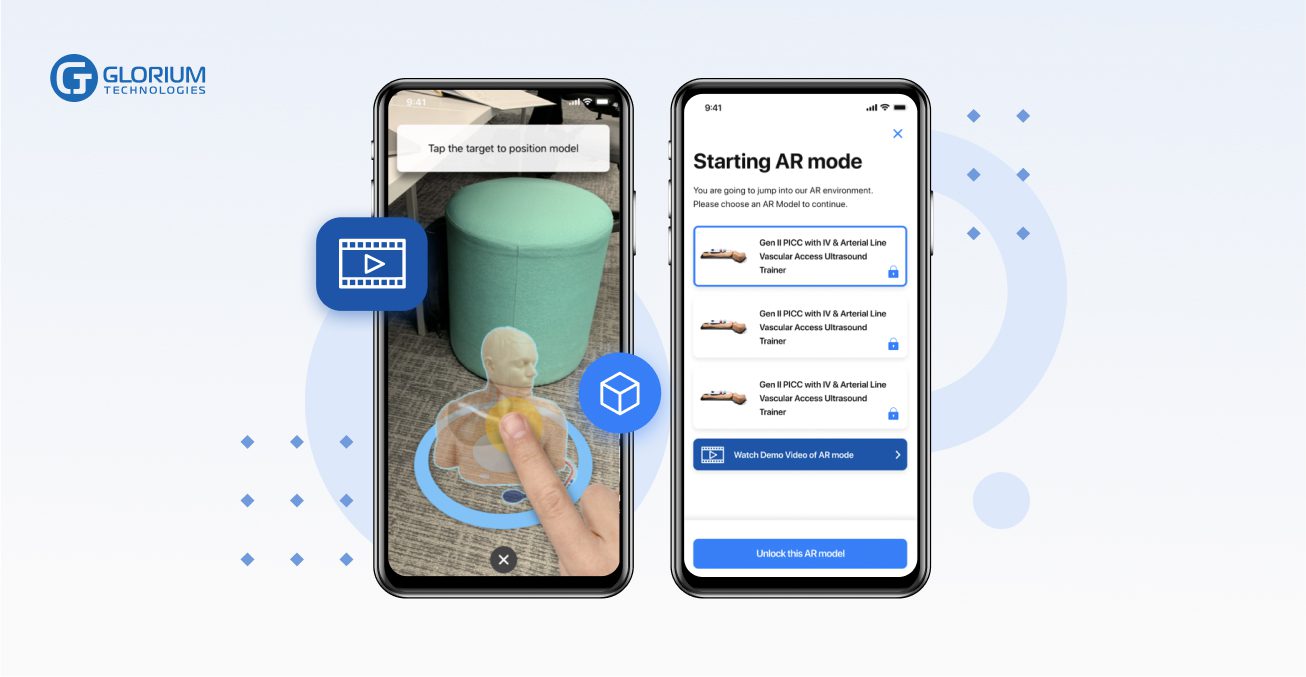
When doctors perform surgery, they can view patient images and scans in augmented reality. It can also be used to help plan prosthetics. Virtual reality visualization benefits patients as well as clinicians, surgeons, and physicians. Healthcare is made more engaging for patients through augmented projections and 3D models. The same is true for orthodontics and other manipulations, where clinicians can show the patient images of their organs before and after surgery.
It also provides an entirely digital environment and superior 3D visualization for a variety of uses. Using virtual simulations, doctors can visualize dose distribution, manage chemical treatments to minimize damage, and improve treatment planning to eliminate risks.
Startups must keep user needs and wants in mind when creating VR and AR interactive solutions in order to successfully implement and adopt these technologies. An attractive and clear visualization of treatment results helps to engage patients the most. The user is given the uncanny feeling of direct participation when an interface is properly designed, and both clinicians and patients benefit from increased trust between them. VR and AR applications must be easy-to-use, engaging, understandable, and fast in order for them to become common and feasible.
So, let’s discover how healthcare software development services can fuel the growth and innovation of your healthcare startup.
Medical software development services offer tailored solutions that cater to the unique needs of healthcare organizations, enabling them to leverage cutting-edge technologies and stay ahead in this dynamic landscape.
From electronic health records (EHR) systems to telemedicine platforms, from mobile health applications to data analytics solutions, we will delve into the key services to transform the way healthcare is delivered.
Electronic health and medical records software are centralized data hubs that store all essential patient information, including health records, visits, immunizations, medications, doctors’ notes, and so on. For EMR software developers, it is crucial to know that there are some essential functions outlined by the Institute of Medicine Committee on Data Standards for Patient Safety (IOM) for the certified EMR. The list of functions includes the following:
As healthcare solutions evolved, new features and functions were added, but the core set remained unchanged. It’s a fact that most software solutions on the market don’t perform as users expect them to, and there’s still plenty of room for improvement. Due to the global pandemic and the intensified digitalization of the healthcare industry, there will be a need for EHR software that is refined, integrated, secure, and high-performing.
 Medical Billing Software
Medical Billing SoftwareHaving a system that can manage claim submissions, track medical billing codes, and provide reporting can significantly improve the efficiency of medical practice. Accounting software automates payment documentation and coding, speeding up financial operations and eliminating time-consuming and tedious manual tasks.
CPT (Current Procedural Terminology) and HCPCS codes are standard categorizations used in medical billing. Each service the clinician provides is assigned a specific code, which a billing system can track and process to determine the amount of payment to be handled.
Clinical communication between clinicians and patients can be simplified with the help of a good medical billing software program that has robust scheduling capabilities.
Learn about Niko Health case study with building in-app billing platform from scratch..
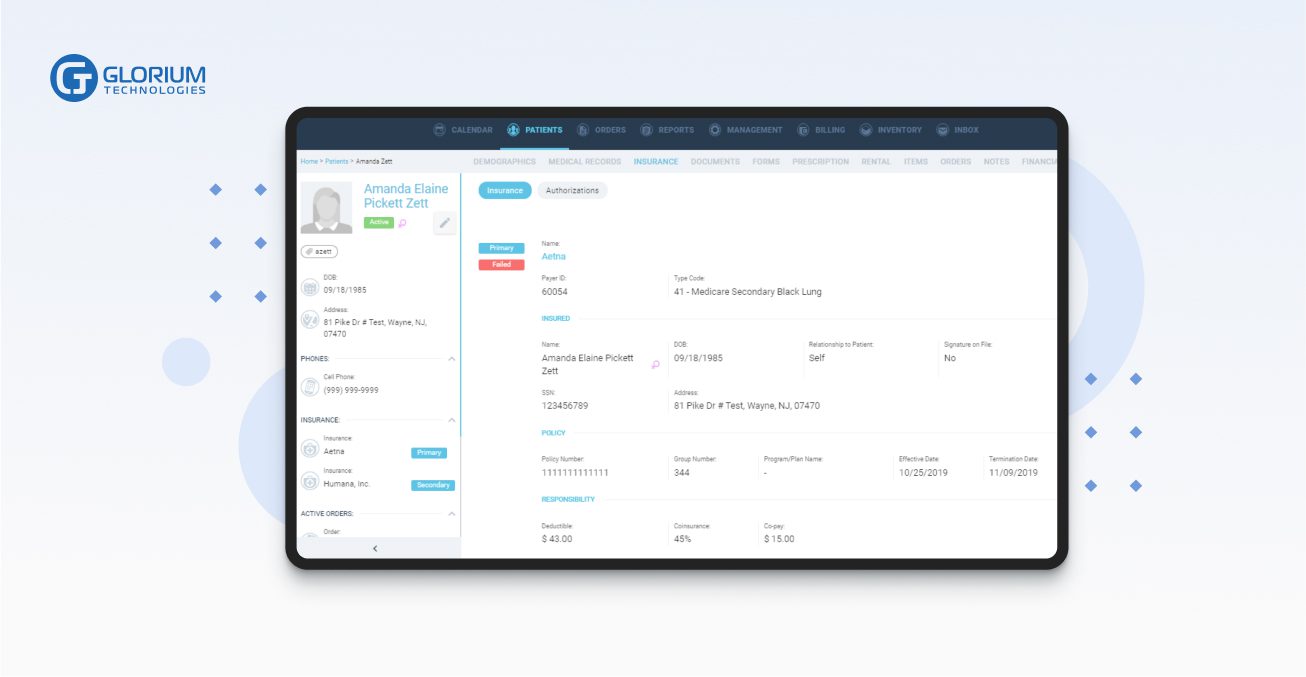
In terms of data management, healthcare is one of the most complex industries to work in. A complex and interconnected network of systems is created each year to both serve a greater number of users and integrate with more software services. In light of the fact that medical information and personal health records are the most sensitive and valuable types of data, managing and protecting them is a real challenge.
As a result of cloud computing, disparate data sources and software systems can communicate with each other. Data collection and sharing are made easier and more efficient for medical professionals with the help of cloud infrastructure. All devices make it easy for clinicians to get the information they need. Cloud computing allows healthcare organizations to centralize data.
The global pandemic acted as a catalyst in pushing the healthcare industry to move to the cloud. Firstly, the majority of medical services have gone online, which means they need a proper digital data workflow. Additionally, cloud infrastructure has provided many opportunities for enabling telehealth, telemedicine, and online consultations, all the while being integrated with EHRs, EMRs, and medical billing systems.
In healthcare, cloud computing has a wide range of applications. Without even mentioning the benefits to patients’ and clinicians’ health and treatment outcomes, it makes it a more connected, engaged, accessible, and collaborative space. Going cloud-based will result in better patient services, lower costs and greater satisfaction among medical staff in the long run.
Healthcare solution developers often overlook the patient’s side of the application, but a clean, safe, and functional patient cabinet eliminates many bottlenecks in the healthcare system, reduces manual and administrative tasks, and instills a sense of trust and credibility in the medical institution. Chatbots and voice assistants can be used to make the support center more helpful and educational.
Patient portals with the necessary information, notifications, and the ability to interact with the doctor are a significant advantage for medical companies today, as more people are willing to be involved in their own treatment process and monitor their health. Patient portals typically include messaging tools, a help center, data infrastructure, automated notifications, and other core functions.
Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS) software is designed to help laboratories manage test results, patient data, and integrate with other healthcare systems to enhance lab efficiency, data accuracy, and bring value to the overall cycle of patient treatment. Here are some essential functions of LIMS software:
By using LIMS solutions, labs can focus on what they do best (science) instead of spending resources developing custom solutions that can be difficult to validate and maintain. A good LIMS system should allow simple configuration to meet individual customer needs and adaptability to a lab’s changing needs.
For biobanks and stability studies, this may include the management of the sample’s entire life cycle, including storage, the chain of custody, and other needs. Additionally, it has to provide samples, tests, and manage information through easy-to-use interfaces with role-based access control. LIMS systems also enable flexible interfaces to instruments and other third-party systems to be available to users. A good LIMS solution adapts to a user’s working style and creates a bulletproof, consistent flow.
Health monitoring is becoming increasingly popular as more people want to be involved in their treatment. Around 80 percent of consumers worldwide already wear or would like to wear a fitness tracking device, according to Business Insider. Medical wearables are expected to increase in popularity as more people become willing to share their healthcare data through tracking devices. Fitness wristbands, however, aren’t the only form of wearable healthcare technology.
Using blood pressure monitors and ECG sensors to track heart rate is one of the easiest and most common applications for healthcare wearables. It can also send alerts and information about a patient’s condition directly to a doctor, such as detecting atrial fibrillation. Meanwhile, patients can receive treatment instructions from their doctors, as well as recommendations. Users’ well-being and the effectiveness of their treatment can be monitored with the help of wearable devices, which also store historical data.
Biosensors represent the next level of medical wearables. Many health indicators such as body temperature, respiratory rate, heart rate, and blood pressure are tracked by these self-sealing patches. It has been shown that the use of such devices reduces cardiac arrest risk in 89 percent of cases, by making them more predictable.
Here are a few examples of health tracking apps made by Glorium:
With the help of health information exchange software, patients, doctors, nurses, pharmacists, and other health care providers are able to access and securely share a patient’s vital medical information electronically, improving patient care in terms of speed, quality, and cost.
Though most medical records are stored electronically, most organizations still store their records on paper or file them in cabinets at doctors’ offices. Patient records are often carried from one appointment to the next by patients who send or receive medical information via mail or fax.
A patient’s past medical history, current medications, and other information are reviewed together during a visit, allowing the electronic exchange of health information to improve the patient’s records, which can have a significant impact on care. Deploying a sophisticated HIE system lets healthcare organizations avoid readmissions, medical errors, duplicates, and other manual inefficiencies.
There are three main types of health information exchange systems:
A customer relationship management (CRM) system is an essential part of the development and growth of any business. A robust CRM helps you keep track of your workflow and make sure all customer information is managed properly. In healthcare, a CRM manages patients and their records.
Medical institutions such as hospitals, laboratories, medical centers, and public or private clinics can benefit from healthcare CRM systems. The best customer management processes can be followed, and client data can be kept up to date with a CRM in healthcare (medical history, visits, medical bills). Medical appointments can be scheduled and tracked using an online medical portal. For daily clinical work analysis, healthcare CRM provides useful reports and metrics that can be accessed through a web browser.
Apart from managing the basic flow, a good CRM enables organizations to proactively manage patients’ health and learn more about their behavior to suggest better care options. It also helps to react faster to patient requests, minimize time spent on operational processes, and automate administrative tasks.
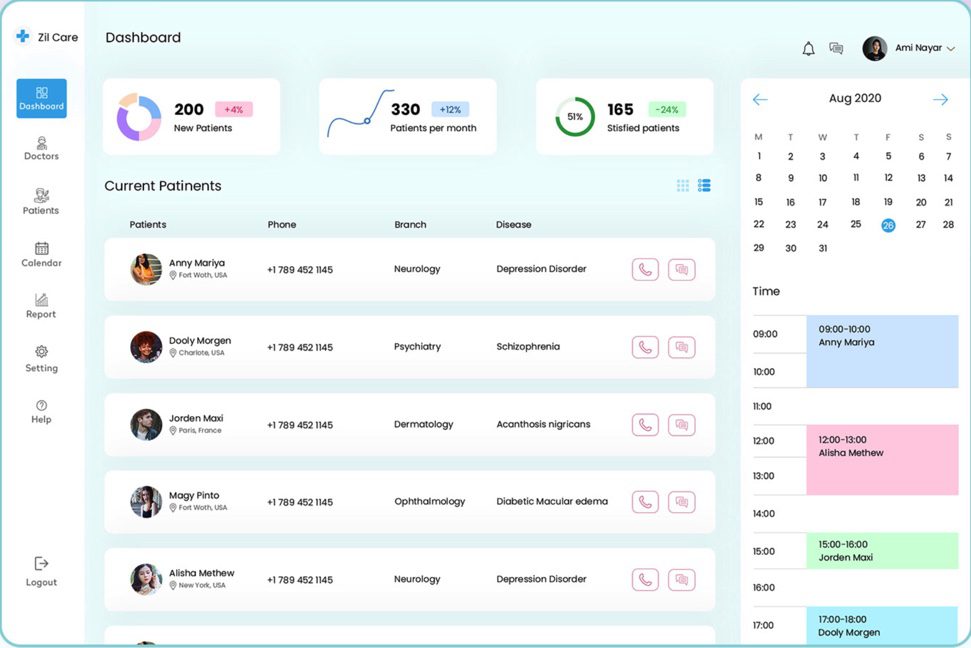 Appointment Scheduling (Booking) Software
Appointment Scheduling (Booking) SoftwareAs part of its appointment scheduling functionality, a good EMR or EHR must offer the ability for clinicians to communicate with patients more effectively.
It is possible to keep track of appointments and doctors’ notes if all visits are stored in the system. In addition, the same feature provides reminders, follow-ups, alerts when lab results are received, and the ability to schedule appointments when it’s convenient for both parties involved.
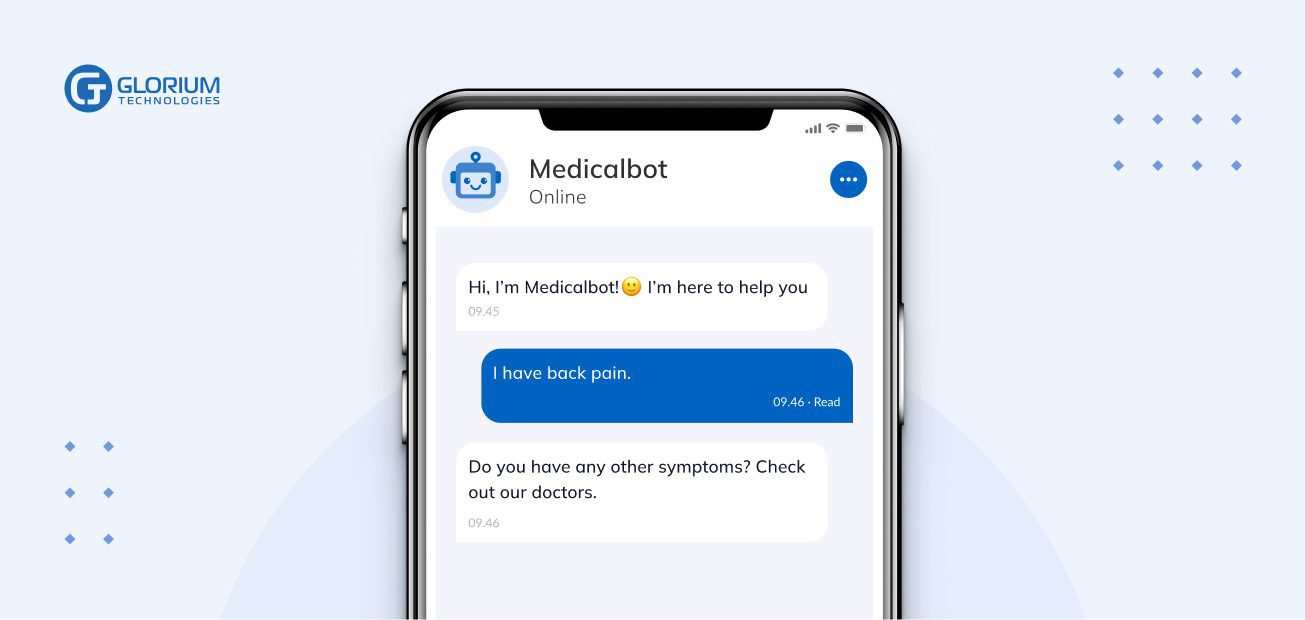
An example of a medical bot’s appointment feature is provided below.
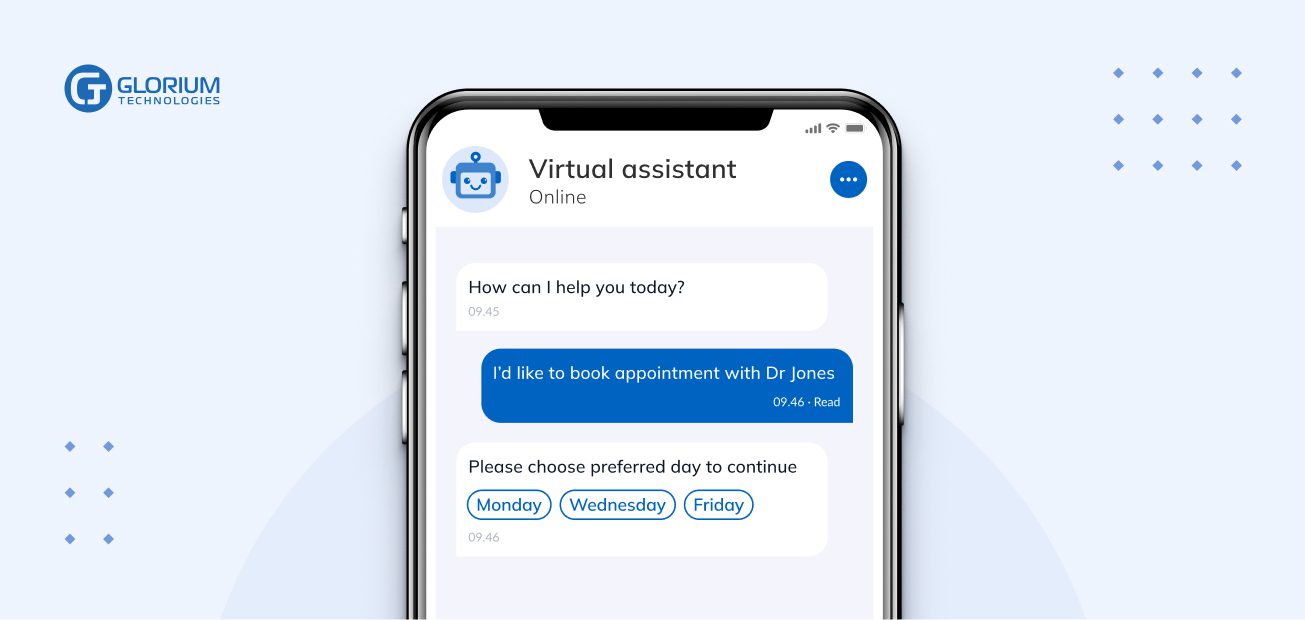
In addition to the pandemic-related increase in usage, the success of telemedicine apps can be explained by their benefits. The US and global healthcare costs have been spiraling out of control for decades, and public accessibility has been a long-standing problem.
Despite this, patient access to quality healthcare has been improved as more practices and clinics offer digital services. Hospitals and doctors also benefit from telemedicine, as it reduces labor costs and increases flexibility.
There are many types of telehealth software solutions, but the most common include the following:
See our best telehealth case studies: Teledentistry solution and Doxy.me.
A set of international standards known as HL7 (Health Level Seven International) is used to receive, exchange, manage, and retrieve digital information between different software applications used by healthcare providers. It’s a sophisticated framework that allows different healthcare data software solutions to integrate and exchange data. Clinical documentation, electronic health records, personal health records, quality reporting, and prescription product labeling are all defined by HL7 standards.
As part of the ISO seven-layer communications model, the HL7 standards are primarily focused on Layer 7 of an application. A system’s communication function is covered by this conceptual model, which is different from the system’s internal structure and technology. A non-profit organization, Health Level Seven International, has created HL7 standards. The American National Standards Institute and the International Organization for Standardization have also adopted them.
FHIR, or the Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources, is a new specification and the latest version of HL7 from Health Level Seven International that can be used as a stand-alone data exchange standard. FHIR specification delivers simplified implementation by leveraging existing logical and theoretical models. Basically, FHIR is the most current framework of healthcare data exchange, made specifically for digital interactions. It enables a modern clinical decision model that covers real-time information access for healthcare providers and connects systems, applications, and devices.
Medical imaging software has transformed the way medical images are captured, stored, and analyzed in the healthcare industry. By providing advanced image viewing, analysis, and workflow optimization capabilities, this software empowers healthcare professionals to deliver accurate diagnoses, improve patient care, and enhance collaboration. With features such as PACS integration, EHR integration, security measures, and remote access capabilities, medical imaging management software is a vital tool that enables efficient and effective medical imaging practices
Read more about medical imaging software development.
DICOM: Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) is an international, nonproprietary standard that specifies the protocols used to facilitate the exchange of medical images and related data within healthcare systems. Medical imaging interoperability is ensured through the use of this global IT standard in hospitals worldwide.
PACS: In medical imaging, Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS) technology provides cost-effective storage, retrieval, and management, as well as the ability to distribute and present medical images. By using PACS systems, images and reports can be transmitted digitally. You no longer must manually file, retrieve or transport film jackets. Images can be captured, stored, viewed, and shared internally and externally by a healthcare organization (such as a hospital).
AI-enabled solutions are now being used to process images and produce faster results in medical imaging, which was previously largely dependent on scanner sensors. Cloud solutions for medical imaging data storage are also gaining in popularity. Healthcare is following the lead of many other industries in adopting cloud computing as a means of storing and sharing information.
We have helped different healthcare providers with AI-enabled solutions. See our BIOMODEX case study and Agfa Healthcare case study for more information.
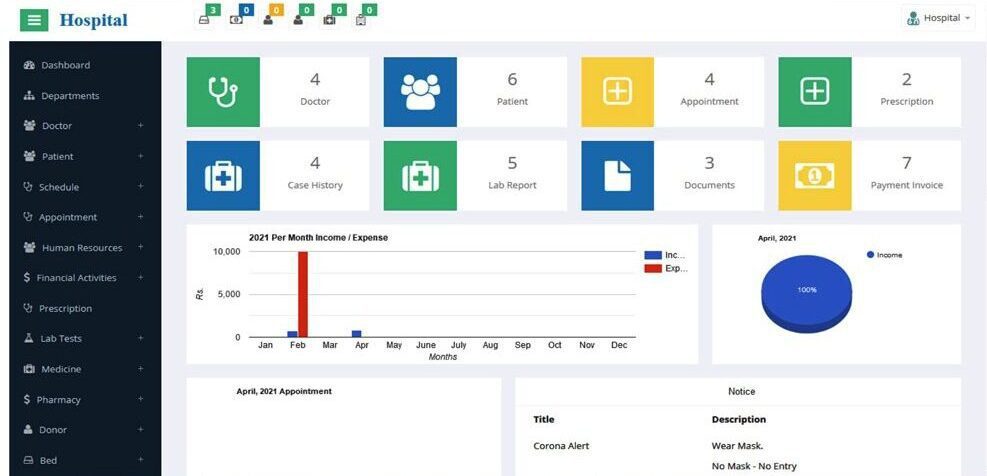
Hospital management software is responsible for monitoring and tracking all the processes within a hospital. The system is used to automate accounting, inventory management, medical billing and claims, patient management, and bed management, among many other tasks and responsibilities.
Let’s describe key features of hospital management solutions.
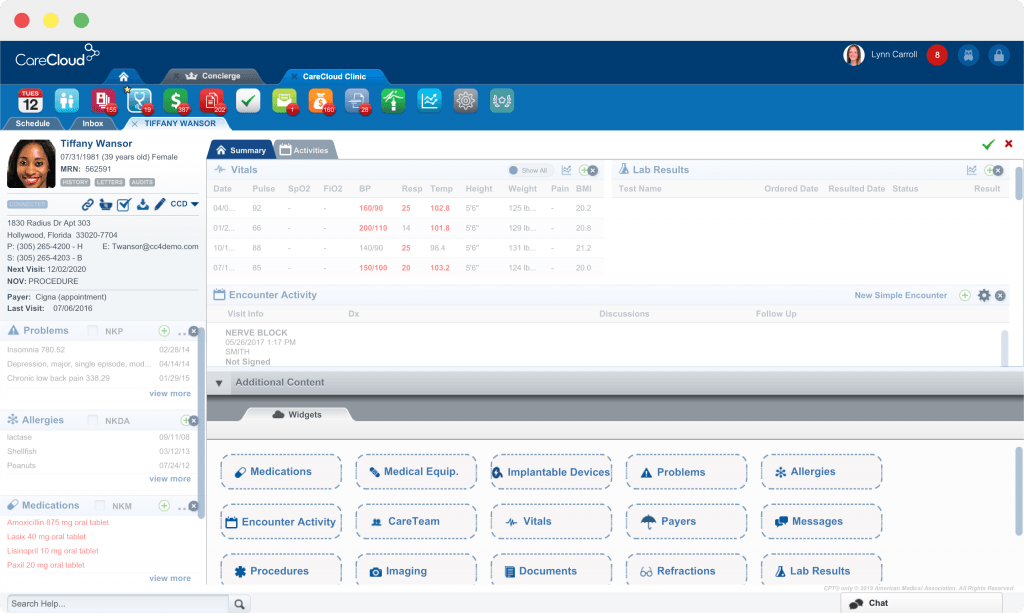
Here is an example of a hospital management interface.
Prescription filling and processing, inventory tracking, and point of sale are the primary functions of pharmacy software. As a result, the software stores important information about medications and patients to ensure that the right prescriptions are given out at the right dosage. Refill requests and insurance verification are also automated by pharmacy management systems. Consequently, pharmacists can spend more time caring for patients and less time on paperwork.
Here are some essential features of pharmacy software:
In order to avoid further health issues, patients must pick up and take their medications on time. Pharmacists rely on pharmacy management software to keep their inventories stocked and their prescription refills on schedule. For patient convenience, the system will also send them reminders to pick up their medications.
When a prescriber submits a new prescription, the pharmacist is notified of the submission. To ensure that a patient’s prescription is covered, the pharmacist will check with his or her insurance provider. The patient will be asked to provide feedback about the side effects of drugs when picking up new medication from the pharmacist to ensure medication is taken correctly.
Healthcare software development costs can vary significantly depending on several factors, including the project’s complexity, the desired features and functionalities, the technology stack, the development approach, and the level of customization required.
Here are some key aspects that impact healthcare software development costs:
By carefully considering these factors and engaging with experienced development teams, healthcare organizations can budget and plan accordingly for software development initiatives.
The first step in building a successful healthcare software solution is to partner with a reputable software development company. Through superior service and tailored solutions, Glorium has more than 10 years of industry experience and can help startups get to market quickly and stay ahead of the competition. Our dedicated team helps you bring your ideas to life by nurturing them from concept to launch.
In exchange for a reduced fee, we offer tech startups the strategic and technical expertise they need to realize their visions. Glorium Technologies has more than 12 years of industry experience and 150+ skilled developers, artists, QAs, PMs, and business analysts ready to dive into clients’ projects. As a result, Glorium Technologies has delivered 50+ products to clients, all of which have been met with complete satisfaction.
Are you ready to take your healthcare organization to the next level? Contact us today to discuss how our healthcare software development solutions can empower your business.
Healthcare development services refer to the specialized software development solutions tailored for the healthcare industry. These services involve creating, customizing, and implementing software solutions to address various healthcare challenges and improve patient care.
Healthcare software can range from electronic health records (EHR) systems and telemedicine platforms to medical imaging management software and pharmacy inventory systems. Customized applications for patient management, appointment scheduling, and analytics are also common in healthcare development services.
Healthcare organizations can benefit from software development services by improving operational efficiency, enhancing patient care, and streamlining workflows. Customized software solutions cater to specific needs, automate processes, and facilitate better data management and analysis.
Healthcare software development can enhance patient care by enabling accurate and secure electronic health records, facilitating telemedicine consultations for remote patients, providing medication management systems, and improving overall care coordination among healthcare providers.
When selecting a healthcare software development company, factors such as their expertise in the healthcare domain, experience with regulatory compliance, security measures, scalability, and support services should be considered. It’s also important to review their portfolio and client testimonials.
Healthcare software should adhere to standards like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) for data privacy and security, GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) for European data protection, and industry-specific regulations such as FDA (Food and Drug Administration) guidelines for medical devices.
Yes, existing healthcare software systems can often be integrated with new software solutions to ensure compatibility and seamless data exchange. Integration enables data sharing across platforms, enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare services.
The development timeline for healthcare software depends on the complexity, the desired features, and the development approach. We can consult you to get a more accurate estimate based on your specific requirements.
After healthcare software development, ongoing support and maintenance services should include bug fixes, updates, security patches, and technical assistance. It’s important to discuss these aspects with the development provider to ensure long-term reliability and smooth operation.
Healthcare software development services incorporate robust security measures, such as encryption, access controls, and regular audits, to ensure compliance with industry regulations. Development providers follow best practices and implement security features to safeguard patient data and protect against potential breaches.








| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |