Reasons to Implement Machine Learning in Healthcare: Case Studies of Those Who Did



According to statistics provided by Oberlo, the machine learning market is growing rapidly. If in 2020 it was estimated at $51 billion, analysts predict that by 2028 it will reach $641 billion, an increase of more than 12 times. For clarity, let’s study the trend of using ML technologies in business. The same resource reports a threefold increase in companies that opted for machine learning between 2015 and 2019.
So why did ML deserve such popularity? In this article, we will understand why this IT technology is so widely used in many areas of modern business, what benefits it can bring directly to the healthcare sector, and what difficulties may arise in its use.
Content
Machine Learning is a segment of artificial intelligence that contains computational, mathematical, and statistical methods for solving problems not under the guidance of a person but, in fact, without their participation. The basis for this is the study of patterns that can be traced in previously performed similar tasks.
AI technologies, particularly ML, are becoming increasingly popular in all spheres of life. Essentially, with the help of ML, AI performs functions that were previously assigned to people but faster, more efficiently, and at a lower cost. According to Refinitiv AI/ML, 46% of organizations use ML technology in several business areas and simultaneously consider it a priority for development.

Machine Learning has a wide range of capabilities:
Thanks to all of the above, ML is used in various industries, including the financial sector (stock trading, e-commerce), customer support services (chatbots), automotive, cybersecurity, and, of course, healthcare. In all these areas, the latest technology guarantees more accurate results in a shorter time.
Let’s consider how ML can help healthcare.
Healthcare professionals need more and more time to process patient information, review patient records, and make diagnoses. The global pandemic was not the last role in this, which caused an uncontrolled increase in the incidence and, accordingly, calls to medical institutions. Scientists from Johns Hopkins University claim that more than 500 million people worldwide have been infected with the SARS-CoV-2 virus so far. An impressive number, isn’t it? But we should not forget about other, no less dangerous diseases, which also require urgent medical attention.
So what to do? After all, human resources are limited by individuals’ physical and mental capabilities – in other words, doctors cannot be at the workplace 24/7, they tend to get sick, and it is vital to rest. And a solution was found. The introduction of ML technologies into healthcare can significantly simplify physicians’ work and allow providing high-quality services to a larger number of patients.
The vast possibilities of artificial intelligence, implemented through machine learning methods, can solve many problems. If we talk about healthcare, these tasks include the following:
Still, doubting that artificial intelligence can be trusted with the life and health of patients? Then pay attention to a study conducted in Korea; according to its results, ML-based software can predict the outcome of Covid19 with over 90% accuracy.

Based on what tasks software developed using Machine Learning technologies can solve in the medical field, let’s consider the benefits of machine learning in healthcare.
According to forecasts, artificial intelligence technologies could cause the loss of 375 million jobs over the next 10 years. But not everything is so simple in the healthcare sector. Doctors note that such widespread use of software based on Machine Learning does not mean that artificial intelligence should completely replace humans in medicine. The new tools are expected to increase the coverage and productivity of the existing healthcare system. This opinion is held by Dr. Tejal Patel, one of the AI/ML research participants.
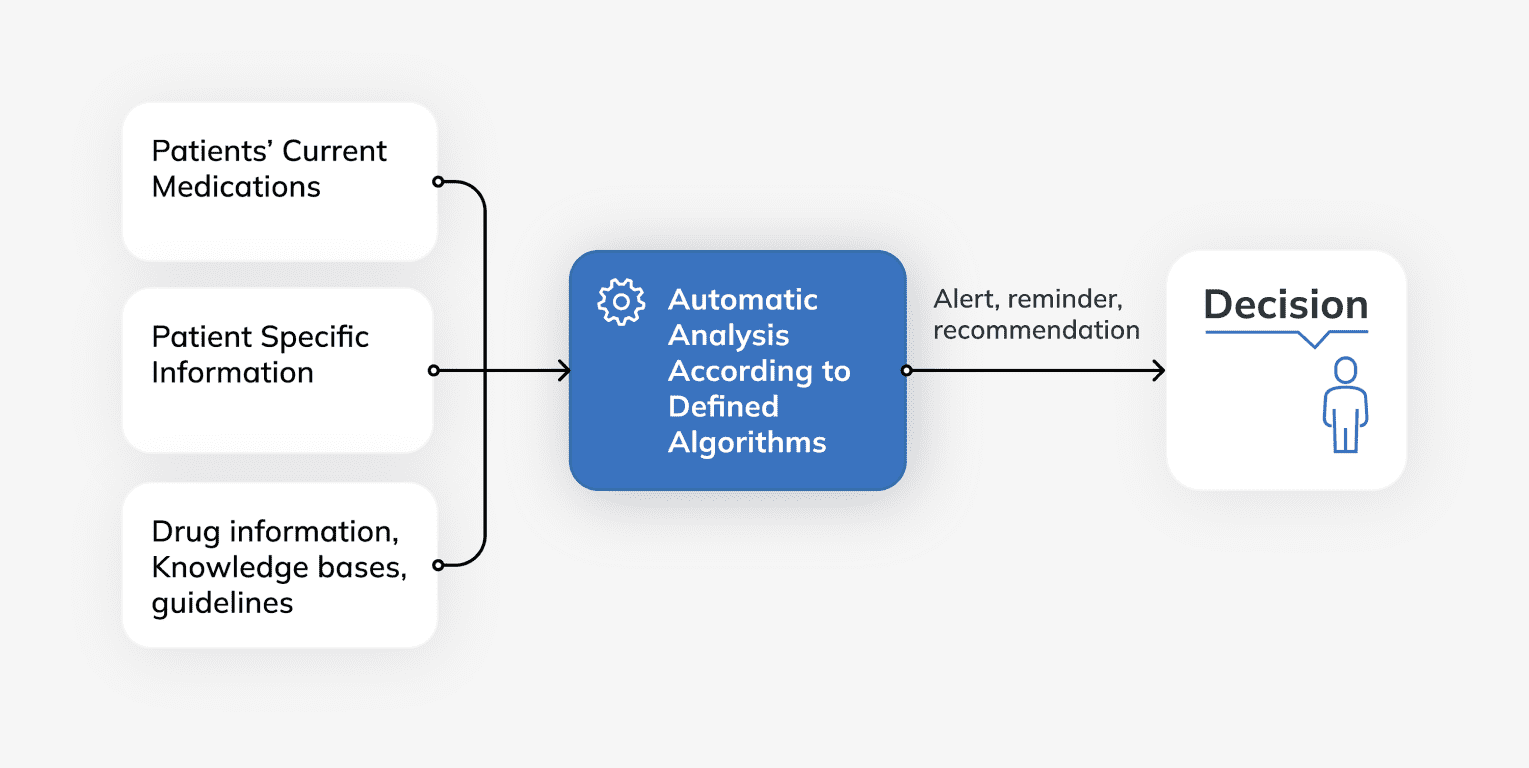
Medical decision support systems are tools based on machine learning technology that helps medical staff make decisions regarding various medical cases. Conclusions regarding certain appointments are based on clinical studies and information about the patient.
One of the first such systems, Leeds Abdominal Pain System, showed excellent results in 1971. It helped establish the correct diagnosis in 91.8% of cases, while doctors were right only in 79.6% of situations.
The completeness of patient data plays a decisive role in making a correct diagnosis. But doctors often simply do not have time to enter constantly updated information manually. It is where optical character recognition technology can come to the rescue, allowing you to recognize handwritten or printed text and convert it into machine-readable files in bmp, jpeg, pdf, and other formats.
The analog format of medical records, including x-rays, in the recent past has complicated the process of studying, analyzing, and conducting new research. But the digitalization of medicine and the use of ML has made it possible to work with this data more efficiently, to identify similar cases, identify anomalies, and select the optimal treatment.
InnerEye software is an example of machine learning in healthcare that allows you to differentiate healthy and tumor cells and plan the course of radiation therapy needed for cancer patients 13 times faster.
Several severe diseases in a patient often complicate diagnosis and treatment. In such a situation, it is essential to consider the compatibility of prescribed drugs and try to minimize their side effects. ML does a great job with such tasks. Thus, the Watson Oncology system not only selects the optimal course of treatment but also offers several options to choose from.
Artificial intelligence helps medical professionals to carry out round-the-clock non-invasive monitoring of their patients. The SafeBeing platform, developed by Somatix, allows you to read the indicators of devices worn by patients and receive data on the state of their health. The functioning of the system is based on reading human gestures.
iCare Navigator is a kind of guide for patients in the world of medicine. The app has broad functionality:
Another company actively using machine learning technologies in medicine is Google Corporation. According to the research results, the company’s specialists developed a diagnostic system, which showed the accuracy of diagnosis by 5% higher than doctors showed in the same cases. The number of false-positive diagnoses made by the machine was 11% less.
Surgery is a branch of medicine that has also been affected by the latest technologies. The first research in robotic surgery was carried out in the 1980s. Today, the use of robotic surgery allows expanding the capabilities of physicians by integrating with a dynamic operating table and performing more operations with a single docking of the robot with the patient.
Helping people stay healthy while minimizing doctor visits is the goal of ML software that helps lead a healthy lifestyle. Examples of such software are the MyFitnessPal and HealthTap apps. Their functions are sending notifications and reminders to patients, answering questions based on previously received medical information, and video communication with the doctor.
This technique is based on the fact that medicine can only be effective if its active ingredient binds to target proteins in the human body. DeepBAR helps quickly identify the connection between a drug and a protein, making it possible to create swiftly effective medications.

Along with the many new opportunities that ML opens up for healthcare, some challenges arise in implementing these technologies.
Some documents regulate the so-called concept of medical secrecy in every state. These are various legislative acts, Civil and, in some countries, even Criminal Codes. But the essence of this concept is the same – everyone has the right to non-disclosure to third parties of information about the state of their health.
It is where there is some inconsistency with the principles of Machine Learning. After all, this technology is based on entering information about patients into the program. And any IT system, by default, implies a small but still a probability of data leakage.
The way out of this situation is maximum anonymity when filling out patient profiles. To make a diagnosis, there is no need to fill in the address of the patients, their financial and insurance information, or phone numbers. The absence of these data will not affect the correctness of the construction of machine algorithms for organizing the treatment process but will allow users to remain anonymous.
One of the functions of medical software is to help people with significant physical and mental health problems. Such apps can form a list of recommendations for maintaining a healthy lifestyle and remind you of the need to take medications and visits to the doctor.
But if we talk about the ethical component of such functionality, there is some violation of the individual’s freedom of choice. People are supposed to follow what the machine tells them strictly. It is necessary to observe the line between recommendations and instructions from Machine Learning to comply with moral and ethical standards.
One of the biggest problems of using ML is the dependence of the construction of machine algorithms on the data that is entered into the system manually. Due to incorrectly entered indicators in the program, the machine may inaccurately interpret the patient’s state of health and prescribe the wrong treatment for them. Such actions can cause not only ineffective therapy but also death.
The solution to this is not possible only at the app level. First, the use of such software should be fully controlled by the attending physician. And secondly, all patients should be initially informed about which method is used for their treatment.
According to a study on racial and ethnic differences in drug response, published in the Journal of the National Medical Association, people of different ethnicities may be resistant to certain drugs or show unpredictable reactions. According to scientists, doctors often undeservedly neglect this human body feature.
To minimize this problem when using ML, it is necessary to organize such training on the experience of as diverse groups of patients as possible.
This problem is because ML is just beginning to be implemented in healthcare, and doctors still do not have enough experience in using it. It means that not all processes created by developers, in theory, will be convenient and effective for actual patient care.
A doctor and nurses are enough to carry out therapeutic interventions in the traditional approach. In the case of using ML, this is not enough. Implementing the technology will require a team of more specialists: a business analyst, an architect, a data engineer, a data scientist, and an ML expert.
This expansion of staffing may bring high financial costs to the healthcare organization, but in the long run, these innovations will pay for themselves, make the work of physicians easier and help provide higher quality services to patients.
Today, the burden on the health care system has increased significantly. To help doctors continue to provide services at the proper level, improve the accuracy of diagnoses and increase the effectiveness of treatment, the IT market offers the introduction of AI/ML software into medical practice. Despite some problems with its app in this area, ML has already proven its worth through multiple successful implementations.