Features to Include in Your Pharmacy Management System



In a diverse world of healthcare services and sectors, pharmacy management plays a critical role. Historically, pharmacy workers have been perceived as consultants and advisers for patients. However, it is challenging to prescribe the right medication without knowing the patient’s health background.
While pharmacists take on the role of the doctor in a limited way, doctors have in a way taken over part of the pharmacist’s role by completing administrative tasks instead of focusing on patient care. Another common challenge is the mismanagement of the clinicians’ prescriptions due to inconsistent data management.
These complications are slowly being resolved as the industry shifts to large and automated pharmacy data infrastructures. It is a vital resource for clinicians and patients that rely on treatment supplies every single day. The Global Pharmacy Management Systems Market is expected to reach the market value of over $35.3 billion by 2027.
According to the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey, 81% of hospital emergency room admissions end up with an urgent need for medicine prescriptions. This means that the pharmacy management system’s role is beyond just aggregating inventory data; it can help detect patterns and provide insights connected to a patient’s medical records.
Because of this, any modern medical organization requires a sophisticated and reliable software solution to manage pharmacy. Pharmacists and healthcare managers rely on pharmacy management software to keep their inventories stocked and their prescription refills on schedule.
Content
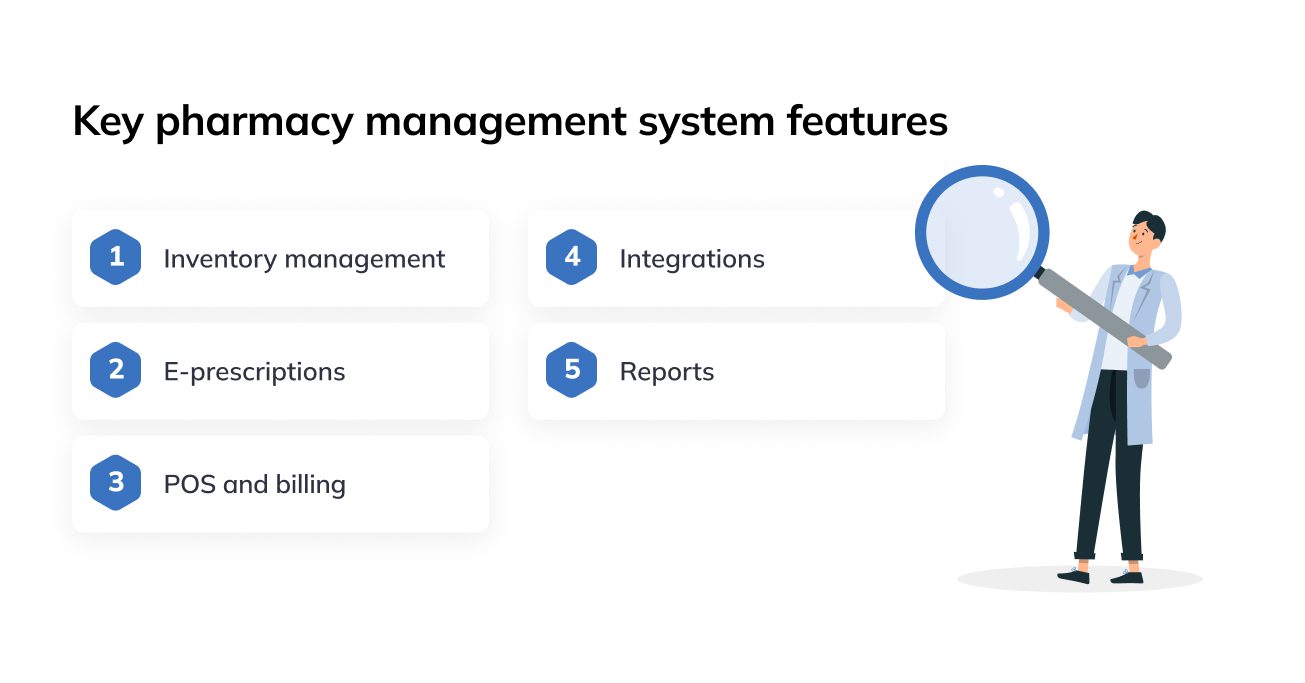
A pharmacy management system is a platform that manages data and processes connected to pharmaceuticals, and basically manages the pharmacy workflow. Prescription filling and processing, inventory tracking, and point of sale are the primary functions of pharmacy software.
Pharmacy management software stores important information about medications and patients to ensure that the right prescriptions are given out at the right dosage. Refill requests and insurance verification are also automated by pharmacy management systems. It also includes following relevant industry regulations and staying in compliance with rules.
For patients’ convenience, the system also sends them reminders to pick up their medications. As a result, the platform enables clinicians and pharmacists to spend more time on their job and less time on administrative tasks and other paperwork.
A pharmacist’s job is full of tedious manual tasks that require precision and a high level of concentration. Synchronizing orders, dispensing drugs, giving out the right medications according to the prescription, keeping track of the stock, and verifying drug eligibility are all time-consuming processes. With such high pressure, it is easy to miss some information or make mistakes.
With a pharmacy management system, workflow is managed automatically. The system matches patients’ historical records to provide background for the right treatment, automatically verifies the prescription eligibility of drugs, sends alerts and reminders, and manages inventory data.
A consistent and automated administrative workflow, in turn, not only facilitates the lives of pharmacists and takes the pressure off them, but also enables better health outcomes to patients.
Pharmacy requires a huge level of responsibility and accountability. Making sure to have the in-demand products in stock, keeping track of every single medication, and managing expiry is no easy task.
Even before the Covid-19 pandemic got into full-swing, drug shortages were a major and growing challenge, with more than 200 shortages annually. Inventory shortages cause increased operational costs and can mean risks for many patients. A PMS can thus identify and prevent shortages before they become a critical issue.
The pharmacy management software has advanced data management capabilities that increase inventory accuracy. It classifies products, checks expiry dates, prepares orders and handles other inventory-related processes.
Pharmacy fraud can take many shapes and forms, from fraudulent marketing, selling fake and dangerous drugs and using medicines for inappropriate purposes, to fraudulently obtaining prescription drugs and monetary scams.

Drug fraud can cost companies millions of dollars, and even lead to lethal consequences for some patients. In fact, drug diversion costs insurers $72.5 billion each year. It is important to have a system that verifies components listed in the medication, verifies vendors, and checks for the FDA’s approval of the particular drug.
A pharmacy management system integrated with the Prescription Drug Monitoring Program database enters data and verifies it when dispensing drugs.

Stock management is one of the most crucial modules within the pharmacy management system. It classifies products, receives and generates automatic orders, manages the goods that are in and out-of-stock, dispenses drugs, prints labels and counts the inventory. Order data is usually received via APIs or EDI, depending on the vendor’s tech capabilities.
Apart from just filtering and managing inbound and outbound orders, stock management includes analyzing patients’ healthcare records to provide the needed order and quantity.
When different drugs are administered to the patient, a great software solution would be to identify which components interfere with each other and send automatic warnings and advice. This kind of solution also ensures compliance and detection of any issues when getting prescribed medications.
Eventually, a PMS also generates reporting of inventory to give suppliers and medical managers insights into bestsellers, and factors that affect drug ordering and distribution.
The ability to prescribe and request medications is a feature most doctors and patients will be looking for in pharmacy management software. Not only does it reduce the burdensome manual prescription process, but also increases treatment safety and compliance.
Through the computerized provider order entry (CPOE) system, when a prescriber submits a new prescription, the pharmacist is notified of the submission. To ensure that a patient’s prescription is covered, the pharmacist will check with his or her insurance provider.
The patient will be asked to provide instructions and information on side effects or drug interactions when picking up new medication from the pharmacist to ensure it is taken correctly. Ideally, all of these processes are handled automatically within the system.
Digital prescriptions greatly increase treatment accuracy and ensures the right medication is given to the right person.
Billing and accounting is a vital part of pharmacy management. Under the sales management module, the system receives orders, collects payments, and gives out receipts, which are later included in reporting.
A critical component of correct billing is accurate determination of products’ codes to request the right price. According to the CMS (Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services), medical coding errors resulted in nearly $16.73 billion of inaccurate payments in 2019.
The point-of-sales module ensures patients have a variety of opportunities to make payments and complete returns. Additionally, a PMS billing should include electronic signatures, loyalty program management, patient data management and financial reporting.
Having access to patient data that is connected to billing history provides opportunities for robust financial reporting. Through intelligent analytics, the software should be capable of making use of patient data and compiling real-time financial reports, as well as providing insights and recommendations on how to improve the patient’s experience.
For data consistency and seamless flow, it is critical for PMS software to have as many integrations with other medical systems as possible. Firstly, there should be an integrated logistics system to distribute medications on-time, and secondly, a PMS should interact with the hospital’s EHR to have access to patient’s treatment records and healthcare history.
Other integrations may include hospital management systems, billing systems, and external platforms, and a PMS should have a secure yet adaptable interface to smoothly communicate with other systems.
Advanced reporting across every module of pharmacy management systems can provide clinicians, vendors, and managers with valuable insights regarding operational performance, sales, customer experience, inventory, billing, and many more.
The interpretation of the acquired information allows for data-driven decisions and provides better service for patients and hospitals, while simultaneously facilitating processes for pharmacists.
The first step towards customized hospital management software is developing and implementing features that meet the industry’s expectations. It is necessary to have a trusted software development provider by your side.
With more than ten years of expertise in health tech solutions, Glorium helps medical businesses address their current challenges and reach the market with excellent service and custom solutions. By nurturing your ideas from concept to launch, our dedicated team helps bring your plans to life.
Learn more about our healthcare software and application development solutions today!