What Is HL7 And Why Does Your Healthcare Product Need It?



Previously, even though all healthcare data was managed with plenty of programming efforts, information exchange was rigid and full of data misinterpretation. As more healthcare organizations have accumulated data from software systems, medical applications, and devices, the need for seamless data integration has increased. In order to achieve interoperability complete with accurate records, these systems must be able to integrate with one another to receive and/or to retrieve new information.
Another pressing challenge is related to the accelerated adoption rate of innovative technology in healthcare. As the demand for technology grows, the need to bridge the gap between healthcare organizations and multiple emerging data sources is more vital than ever. In order to simplify the process, the non-profit organization, Health Level Seven International, developed a unified data exchange standard with the sole purpose of simplifying information sharing throughout the healthcare industry. Presently, It has developed several standards (with HL7 being the most prominent), and a recent substandard, FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources). These standards have been adopted by the American National Standards Institute and International Organization for Standardization.
Content
HL7, or Health-Level-7 (developed by Health Level Seven International), is an internationally accepted set of standards that serve as a medium to receive, exchange, manage and retrieve digital information transferred between different software applications used by healthcare providers. In short, HL7 is a sophisticated framework that allows various healthcare data software solutions to integrate with each other and interpret data. The HL7 standards consist of a number of flexible guidelines and methodologies with which various healthcare systems use to communicate with one another. These guidelines and data standards ensure that data exchange rules and common health data definitions relating to clinical documentation, EHR and personal health records, quality reporting, and prescription product labeling remain consistent across systems.
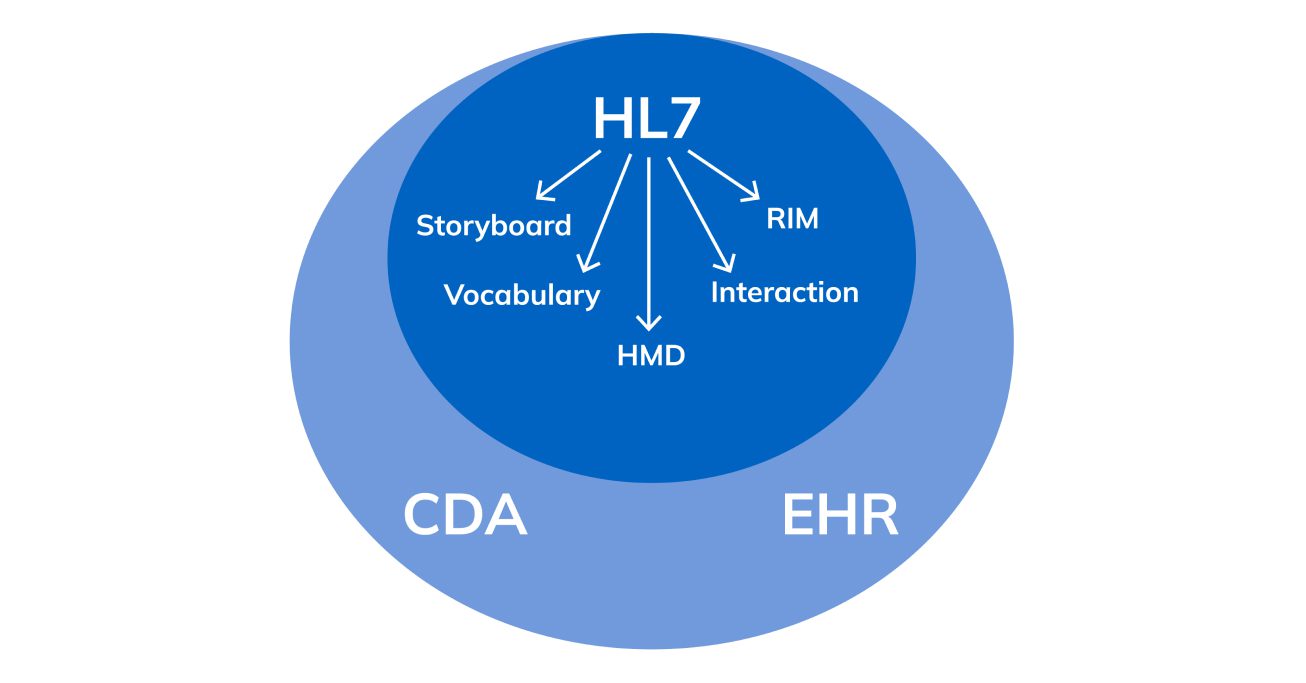
The HL7 standards primarily focus on the application layer (layer 7) in the Open Systems Interconnection of the ISO seven-layer communications model. The application layer is a conceptual model that covers the communication function of a system with no regard to the internal structure or technology.

There are certain HL7 standards (categories, versions, and concepts) that are predominately used for HL7 system integration. The following is a list of where some of the primary HL7 standards belong:
Health Level Seven International has been improving its product constantly since the first version of HL7v1. So, several new versions saw the light: HL7v2, HL7v3, and the FHIR substandard. To understand how the product has improved over the years, let’s take a closer look at the versions:
In order to ensure everyone’s voice is heard, Health Level Seven International develops its standards via a balloting system. This democratic system allows members to vote and comment during successive balloting rounds until there are no negative comments left and draft standards are agreed upon.
While the HL7 protocol enables data sharing and exchange, the HL7 interface is an interconnection that allows for information transmission between different system endpoints.
In order to allow this exchange to occur, healthcare companies need to integrate and enable their data systems with the proper means of communication.
Developing a new standard is a fairly complex and time-consuming “run” for specialists. The process of integrating hospital services into the system is a little easier, nevertheless, it is also a meticulous task. But having hard and flexible skills of IT specialists together with the right technology stack helps to overcome the difficulties with a minimal waste of time – 1 to 3 months.
Let’s take a look at the basic steps for launching HL7 in a medical facility system:
Interaction between systems is a key point in the integration process. It is necessary both to optimize and improve the work of the staff, as well as to correctly display information from other sources. By planning a system interface correctly, you can avoid data duplication and achieve compatibility between different apps.
Among the most common interfaces are distinguished:
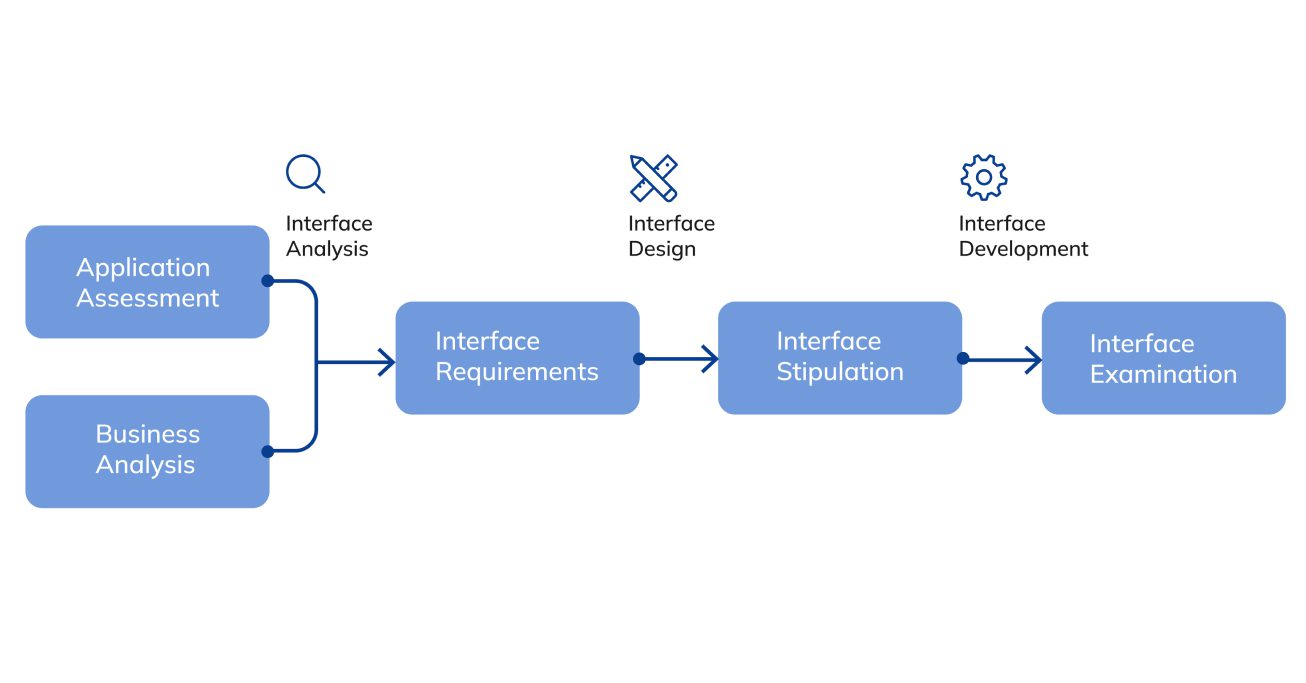
Interface engineers are involved in the process of developing the connection between user and system. Their competence includes not only the creation but also initial testing with further development of ports on an application side.
A technical specialist works according to the following plan:
Testing of the created interface is the final stage of HL7 implementation. At this step, the technical specialists and experts in that field of activity for which an application was developed get involved in the work. The involvement of these experts is necessary to obtain a full-fledged analysis of the system’s appearance, usage algorithm, and content.
There are two types of testing:
Proper data sharing and interchangeability play a crucial role in the healthcare industry. As medical institutions continue to adopt more software and devices, it is crucial to ensure smooth data integration between all systems and disparate data sources. Depending on the data, there are various types of HL7 messages that are transmitted between systems. HL7 is primarily used by hospitals, private clinics, governmental healthcare institutions, healthcare software providers, laboratories, pharmaceutical companies, and other patient care and medical facilities.
After understanding the question “what is HL7 in healthcare?”, let’s define the categories of users of the global standard. Depending on the data, there are different types of HL7 messages that are transmitted between systems.
These are mainly hospitals, private clinics, public health agencies, health care software vendors, laboratories, pharmaceutical companies, and other patient care and medical facilities.
There are other categories of professionals who use HL7. Nominally, they can be divided into three groups:
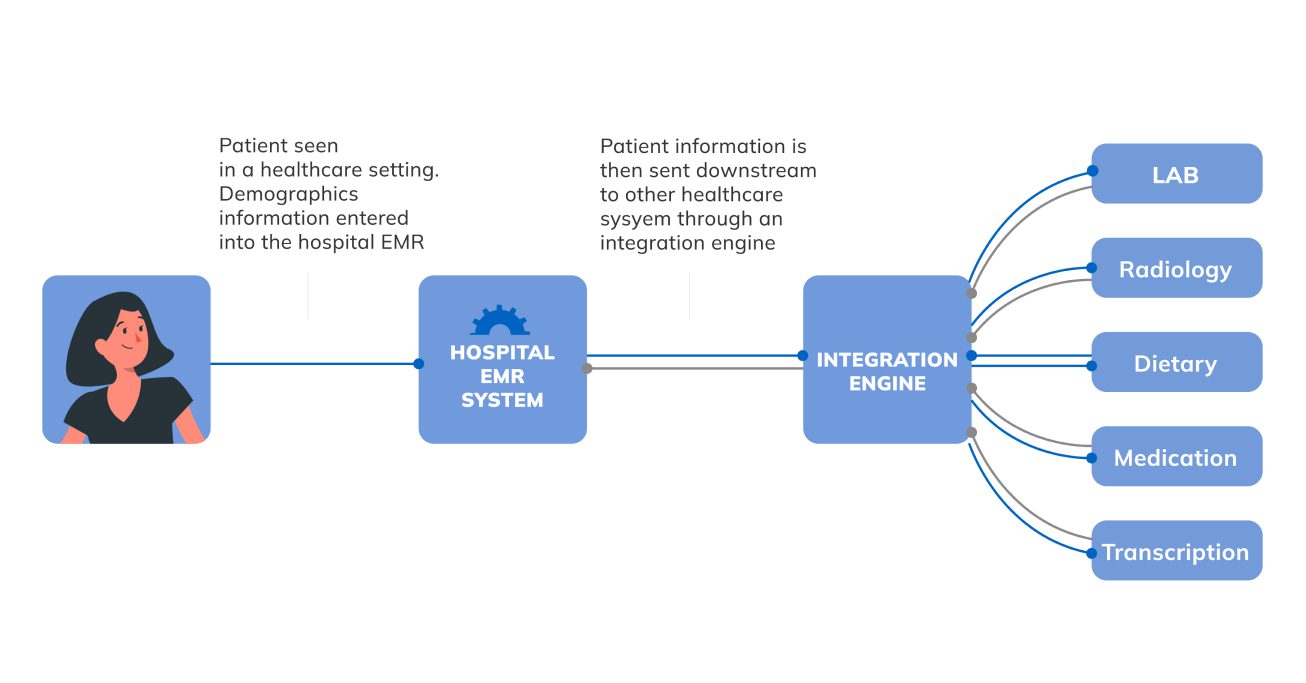
The modern healthcare industry operates multiple systems and devices to sustain its essential day-to-day operations. All of these software solutions and applications are built differently, designed with different functionality, capabilities, and features. The challenge here is that some organizations use large, complex data infrastructures and essentially operate using massive volumes of information, while other healthcare institutions deploy more simple software solutions. The purpose of the HL7 standard is to create a universal protocol so that any organization with permission can access and retrieve information from other healthcare software systems or applications.
Although electronic health record (EHR) systems are the most common and widely used solutions for workflow automation, it is often challenging to properly communicate between various EHRs and other data sources, including lab services, pharmaceutical systems, etc. Here, HL7 standards can help enhance interoperability and transmit data whether the systems use older communication paradigms or modern APIs. Additionally, HL7 can serve as a tool for workflow automation if a hospital or medical organization doesn’t have a comprehensive EHR. The protocol itself structures and shares data in a clear way, thus simplifying the information exchange process throughout the healthcare industry.
As HL7 serves as a powerful tool for storing and exchanging healthcare data, it has potential for global use and collaboration. One of the ongoing issues in the healthcare industry involves collaboration between established governmental institutions and the rapidly growing health tech sector along with private practices. Health-Level-Seven standards create a unified guideline for all healthcare market players, including private clinics, state hospitals, laboratories, and healthcare software providers, enabling them to cooperate faster and more efficiently. In addition, HL7 protocols play a crucial role in times of international health crisis, for instance, throughout the global COVID-19 pandemic.
Improved communication between different medical organizations allows for the accumulation of more valuable data that can be leveraged to improve the quality and efficiency of a patient’s care. HL7 enables faster and smoother data exchange which allows clinicians to receive up-to-date information and get a wider clinical perspective as more patient records are available for access.
Through HL7, clinicians have access to relevant information from multiple sources and can be sure that all data is synchronized and relevant. With a reduced need for requesting and filling out information manually, HL7 standards save time and ensure higher accuracy when dealing with patient records.
Apart from seamless data transmission between existing systems used by particular medical institutions, the HL7 protocol also opens more opportunities to experiment with other software solutions. This not only creates a wider pool to choose from but also enables flexibility in terms of tech solutions for healthcare companies.
No matter who says what, there are vulnerabilities in any system. It is almost impossible to create a multitasking and multilevel product that is perfect from all sides. And HL7 is no exception.
Oddly enough, the main weakness of HL7 is its key characteristic – flexibility, which allows different workspaces to “communicate” with each other, applying new variations and elements of HL7. But at the same time, the adaptability of the standard complicates the processes of information transfer between unrelated structures.
Also, the work of the standard is challenged by the release of updates, which include new features and aspects of the work. On the one hand, this helps to improve HL7, but on the other hand, it complicates it. But new interface tools have been introduced to solve this problem. Like international conferences, where everyone understands each other through “interpreter” devices, HL7 has mechanisms to transmit and receive information simultaneously.
Different medical institutions operate different apps, so each one has its own unique features. When using HL7, these must be considered to ensure that all protocols work smoothly. At this stage, the HL7 standard versions have some weaknesses, but IT experts skillfully compensate them with additional solutions. Perhaps in the near future, the technology will improve so much that specialists will be able to make HL7 an absolutely perfect tool for transmitting information around the world.
Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources (FHIR, pronounced ‘fire’), is a new specification and the latest version of HL7 from Health Level Seven International that can be used as a stand-alone data exchange standard. The FHIR specification delivers simplified implementation by leveraging existing logical and theoretical models.
FHIR uses a modern clinical decision model that provides healthcare providers and individuals with real-time information access and connects systems, applications, and devices. The main aim of FHIR is to deliver resources that can support the majority of use cases either by themselves or when combined.
Learn more about – FHIR vs HL7 v2: Key Difference in Healthcare Data Exchange Standards.
Medical data are among those that fall under the category of “confidential”. Doctor-patient confidentiality prohibits specialists from sharing patient information with third parties. Because of this, systems for transferring data between institutions and specialists need good data protection.
It is important to note that during the analysis and verification of the installed interface, test data from the working environment is needed. Without it, it is impossible to determine whether the connection works correctly. All this information during integration “settles” on computers and laptops of technicians. Therefore, this stage also needs the protection of patients’ personal data. After all, no one is immune to losing a gadget or a hacker attack.
To avoid attacks on confidential data, specialists resort to anonymizing test information. So, pseudonyms are used, birthdates are generalized, and direct data (names, social security numbers, addresses) are deleted.
Communications and information exchange in the HL7 system can be protected by various security programs: from encryption to SSH tunneling. The simplest option is to use VPN services. HTTPS, SFTP, FTPS, and SMIME protocols are also used for data transfer. The HL7 system even has special “drafts” to work over them.
Because HL7 is a two-way “cooperation”, you cannot always control both parts. The transfer layer, together with the client app, must be equally well secured. Secure transmission of information can be provided by SSH, SSL, TLS protocols.
HL7 will remain a central standard for healthcare software development. As the need to remain compliant with updating HIPAA regulations and integrate with multiple software systems grows, its role will only become more critical in the near future. Glorium has more than 10 years of experience developing solutions for healthcare organizations. Allow us to provide your team with our professional expertise when it comes to implementing HL7 protocols into your applications.
Learn more about our solutions or book a call today!
The HL7 standard allows hospitals, laboratories, and other medical facilities to quickly retrieve data from disparate sources and synchronize and share it with other systems. So, clinical specialists can see a patient’s complete and authentic medical record or up-to-date information about the latest tests, treatments, etc.
First and foremost, it’s getting the information you need quickly. Using HL7 also has the following benefits:
Each of them has its unique and strong characteristics. HL7v2 is easier to implement and use, while HL7v3 has a robust and extensive data exchange standard. FHIR is easy to implement and integrate with previous versions of HL7.
When selecting the right option, rely on your organization’s goals. And for successful integration, consult with a technical expert.