How To Implement ERP Software for Healthcare: Features, Solutions



More and more, hospitals and medical companies have begun shifting from legacy systems to modern, adaptive solutions.
Content

ERP, or Enterprise Resource Planning software, is a software application system for integrated, real-time cross-department resource management and distribution. ERPs are designed to manage core business processes, including cash flow, revenue cycles, procurement, and planning. Now more than ever, ERPs play a much bigger role across the modern workflow of the healthcare sector.
ERP is essentially an infrastructure that standardizes, simplifies, and integrates corporate operations across finance, human resources, procurement, distribution, and other departments. Hospital ERP systems typically run on an integrated software platform, complete with shared data definitions under a single database.
Initially, ERPs were created for the manufacturing industry, but as it proved so versatile, it quickly spread to many other verticals, including governmental structures, financial institutions, the hospitality industry, and eventually, the healthcare industry.
ERPs were designed to manage finances across departments, but the current capabilities of these software solutions is much more vast. Furthermore, depending on the industry, hospital ERP systems can be centered around specific features that are required for a particular business.
When it comes to healthcare, hospital ERP systems act as a centralization hub for the majority of operations across departments, including staff management, patient care, clinical operations, billing, pharmaceuticals, laboratories, etc. Though the healthcare industry boasts a moderate adoption rate compared to other industries, its adoption will continue to grow in the upcoming years.
For many hospitals, having a well-implemented Hospital ERP system means fewer errors, reduced costs, organized and streamlined resource management, and an overall smoother workflow.
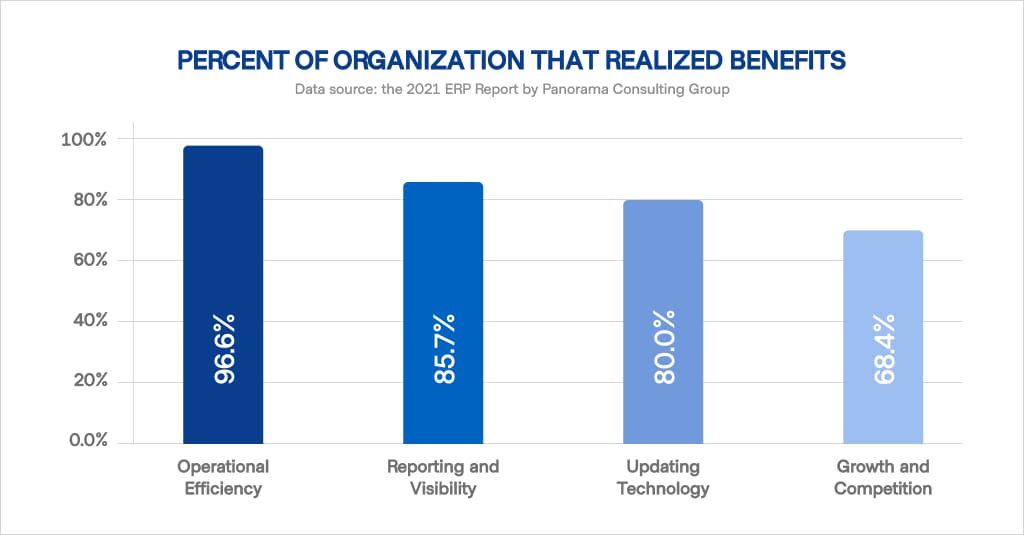
The successful implementation of ERP into the workflow of a healthcare facility has many proven benefits. Mainly, its contribution involves better operational efficiency, facilitated reporting, and visibility across business processes. In essence, it is directly responsible for improved patient care, and ultimately, the growth of the sector and its profitability as a whole.
A common data infrastructure allows for a streamlined workflow, data security, and fewer administrative errors. Needless to say, it drastically reduces operational costs and lessens the burden felt by clinicians. With an automated ERP system, there is no need to manually enter and reiterate the same information over and over, across disparate systems.
When implementation is executed correctly (and the staff is open to leveraging the new technology), an ERP works wonders when it comes to staff efficiency. Business-wise, ERP implementation enables visibility and allows senior leaders to take strategic planning to the next level.
Having a centralized dashboard complete with operational and transactional data allows users to define potential gaps and develop a solution to cover them. ERP makes it much easier to spot areas for improvement and/or systematic patterns that circulate in departments or verticals.
It also has significant implications for patient care. The proper management of healthcare data allows facilities to improve their customer service and quality of care. Physicians find ERP exceptionally useful when it comes to gaining insight into patient treatment. Furthermore, executives gain access to analytics on important business processes directly related to the increase of business intelligence.
An ERP software solution development enables clinicians to avoid numerous time-consuming entries and paperwork — patient info only has to be entered once. After registration, personal data is automatically transferred to the required department and added to the new health records.
When it comes to scheduling appointments, a system suggests available time-slots that are aligned with a practitioner’s schedule and books the appointments beforehand.
Revenue cycle management is a fundamental feature of any ERP, especially in healthcare. Refined financial management reduces the number of errors resulting in operation and labor cost savings. As the system documents and smoothly transmits transactional data, there are fewer issues with billing and budget overruns.
Modern ERP should handle order entries and invoicing from various payment channels, validate financial information, and smoothly run transactions across business units and departments.
Additionally, an ERP should have a POS profile in place to reduce the need to manually log into multiple systems.
Enterprise-wise, integration is a critical feature of ERP that enables cross-department connectivity and integration between various company units. In practice, this looks like a quick and smooth end-to-end process, from an order entry to a finalized invoice.
Each department produces volumes of data. This can be a source of errors and monetary losses. An ERP is designed as a single hub for all data streams to unify and streamline information across multiple departments. It also enables a hierarchical unit structure where an appropriate module is assigned to a responsive unit when an entry emerges.
Inventory and procurement are a critical part of a hospital’s workflow. As such, the capacity to manage lab results, pharmaceuticals, equipment, and the order-to-cash cycle is an important feature of any ERP.
Automating these processes ensures accurate prescriptions, test results, better patient care, and lower costs for an organization. It also reduces the probability of delayed deliveries and lowers the chances of running out of supplies.
It’s hard to find a more painful issue in healthcare management than compliance. As regulations are constantly changing across many healthcare branches, keeping track of updates and complying with current rules is critical.
ERP software development should enable automated, AI-driven compliance management to alert the system and initiate change automatically. This way, medical facilities can focus on their core competencies rather than spending hours checking for compliance updates and reestablishing regulations within the company.

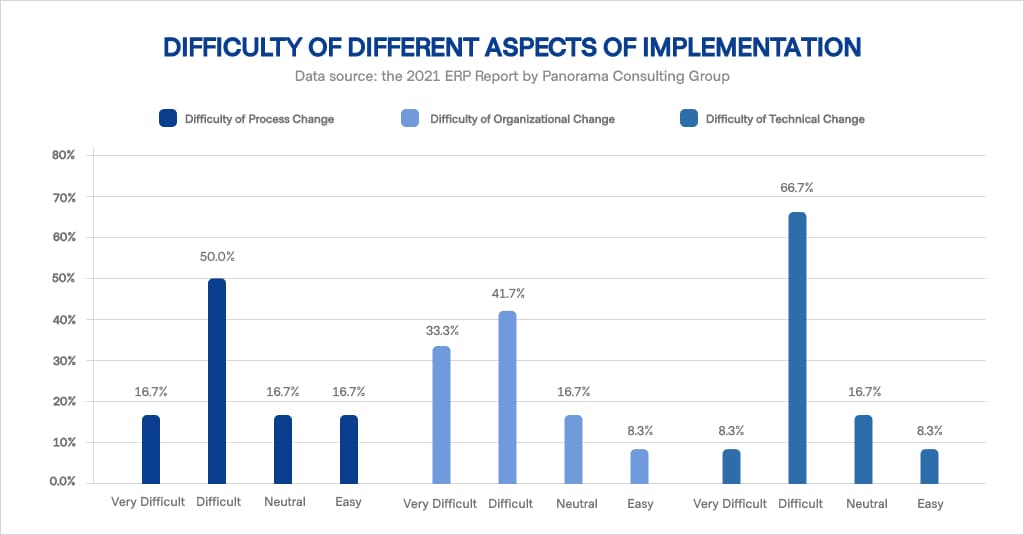
Implementing ERP is a complex process. As it requires a change of business processes, it often involves the redistribution of roles within an organization, the alteration of job responsibilities, and changing the overall interface.
This process requires tight coordination, support, and structure. Hospital management or organization investors who look to implement ERP medical software can rely on the following process to incorporate this software into their business model.
Ultimately, when it comes to selecting the best vendor that will understand and consider the particular needs of a company, it’s better to set your eye on experienced providers with specific expertise in the healthcare sector.
The first step toward customized hospital ERP medical software is developing and implementing features that meet the industry’s expectations. To accomplish this, it’s necessary to have a trusted software development provider by your side.
With more than ten years of experience with health tech solutions, Glorium helps medical businesses address current challenges to hit the market running with excellent service and customized solutions. By nurturing your ideas from concept to launch, our dedicated team is guaranteed to bring your plans to life and build a sophisticated hospital ERP.
Learn more about our healthcare software and application development solutions today!
ERP is essentially an infrastructure that standardizes, simplifies, and integrates corporate operations across finance, human resources, procurement, distribution, and other departments. Hospital ERP systems typically run on an integrated software platform, complete with shared data definitions under a single database.
It implements all features that meet individual business requirements. Customized ERP standardizes, simplifies, and integrates corporate operations across finance, human resources, procurement, distribution, and other departments.
Firstly, an executive gathers all necessary documentation and requirements for the software. In the case of private businesses, key information is collected, including problem definitions, software goals, scope, risk, benefits, and of course, implementation costs and estimations. Once the document is formally approved by the responsible figures, the process is ready to start. Then create a plan (technology upgrades, a project timeline, and a breakdown of resources. As the most complex and practical stage of implementation, there is setting up new parameters for the upgraded workflow. Additionally, in this phase, developers tackle possible integration issues. They also migrate data, test the software, and finally, complete all necessary system upgrades. Before the new ERP goes into full swing, it’s important to finish the preparation process to get the most out of the new solution. This includes staff training, setting up maintenance and support, additional testing, etc. Once these important processes have been completed, it’s time to test the ERP system.