Healthcare Business Intelligence (BI): Benefits, Features



Today healthcare facilities produce, process, and store more data than ever before. Electronic patient records, financial metrics, industry health statistics, patient satisfaction scores, clinical trial data from pharmaceutical organizations, and insurance information are all the data to be analyzed on a daily basis.
That is why more and more hospitals are switching to digital tools for healthcare business intelligence. The healthcare BI market is projected to exhibit a CAGR of 14.05% by 2027.
What is BI, and what does it mean for medicine?
Content
The term “business intelligence” was coined back in 1865, and now, 156 years later, it is difficult to imagine a modern enterprise without a BI system, especially if it often deals with large amounts of digital data.
The digital BI system plays an essential role in collecting, analyzing, and processing business information in various fields of activity.
BI includes methods, tools, and technologies to transform disparate information from different sources into helpful and understandable analytics. You can track results and make business decisions based on this data.
The benefit of such analytics is difficult to overestimate, as it can be applied both at the whole company and its branches, divisions, or even individual products.
In healthcare, BI is one of the most important tools for managing medical data of all kinds: from electronic medical records to unstructured statistics from the Internet or patient information from IoMT (Internet of Medical Things).
There are no restrictions for business intelligence: data collection is possible from both healthcare providers and outside institutions.
Business intelligence allows a hospital, clinic, laboratory, and other healthcare institutions to organize the most significant categories of data: financial, operational, and clinical.
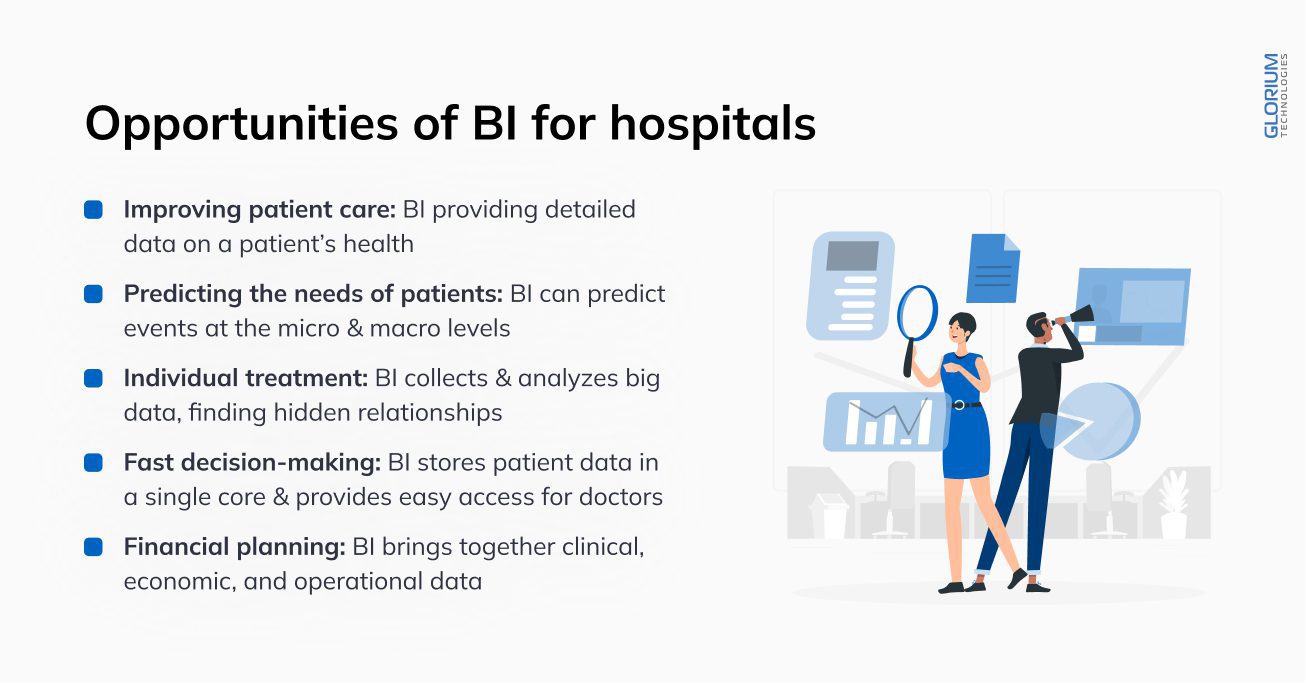
This data becomes the foundation for improved patient care, better treatment efficiency, reduced costs, and quick accreditation of healthcare services. And all this is possible with the wide digital capabilities of BI systems.
For the general user, e.g., doctor, nurse, medical registrar, laboratory assistant, or pharmacist, the principle of healthcare BI solution looks quite simple and consists of 3 stages:
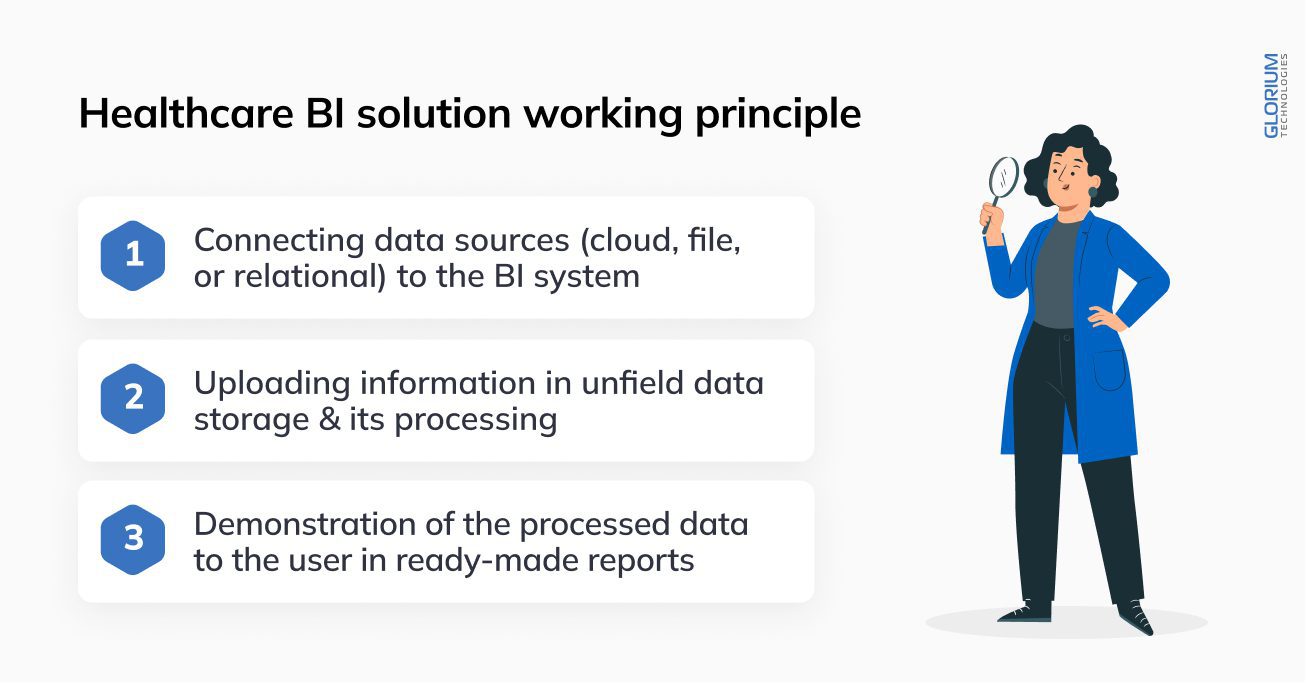
To use BI, a healthcare professional does not need to have special technical knowledge and skills. With an intuitive interface, you can quickly query the reports you want and access analytics.
As a response to a user’s request, the system generates a dashboard: an information panel with grouped data presented in a convenient visual form: tables, graphs, charts, and reports.
The peculiarity of healthcare BI tools is that all displayed data is interactive: the user can view it, edit, enlarge it, or rebuild it at their discretion. You can study in detail the research results at the macro and micro levels, evaluate each indicator individually, and track the dynamics of changes over a specific period.
Although the system is easy to use, it is based on complex algorithms for processing data and creating advanced analytics.
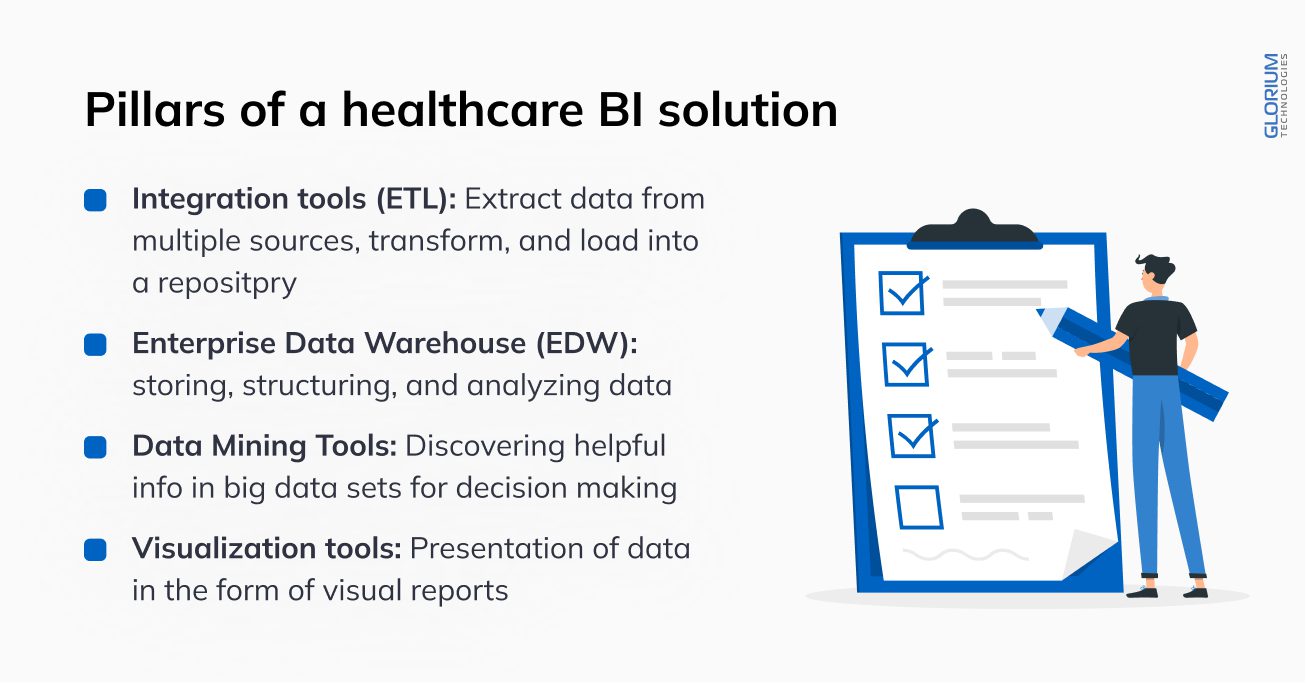
The business intelligence system integrates external and internal data. It allows hospitals to eliminate 90% of the routine when working with analytical data and producing operational and strategic reports.
Business intelligence software for healthcare can be a stand-alone decision-making tool. It integrates with any corporate software, quickly adapts to the needs of private and public institutions, and supports all types of analytics.
Healthcare analytics is used for generating reasonable assessments that help the healthcare institution make the right decisions and develop a business strategy. Depending on the species, the analyst can answer the questions:
Using business analytics, healthcare professionals can collect data and conclude the current situation in healthcare facilities and possible developments.
It is the key to improving work processes at the institution levels, branches, and departments.
The world knows many examples of business intelligence in healthcare with impressive results. The University of Pittsburgh Medical Center predicted flu season incidence and readmissions;
Colchester Hospital cut reporting by 177 hours per month, Carilion Clinic identified heart disease risks among 8,500 patients, and Keystone significantly reduced the number of accidents.